Overview of Mifare Classic Tags
Mifare Tags are used for public transport tickets, electronic door keys, medical security cards, smart cards and other things. In this article, I give an overview of Mifare Classic Tag.
𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐧𝐭 𝐨𝐟 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐚𝐫𝐭𝐢𝐜𝐥𝐞:
- 𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐌𝐢𝐟𝐚𝐫𝐞 𝐂𝐥𝐚𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐜 𝐑𝐅𝐈𝐃 𝐓𝐚𝐠
- 𝐌𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐲 𝐬𝐭𝐫𝐮𝐜𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞 𝐨𝐟 𝐌𝐢𝐟𝐚𝐫𝐞 𝐂𝐥𝐚𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐜 1𝐊
- 𝐌𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐲 𝐬𝐭𝐫𝐮𝐜𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞 𝐨𝐟 𝐌𝐢𝐟𝐚𝐫𝐞 𝐂𝐥𝐚𝐬𝐬𝐢𝐜 4𝐊
- 𝐀𝐜𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬 𝐑𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐭𝐬
- 𝐈𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧
What is Mifare Classic RFID Tag
Mifare Classic Tag is a protected memory storage device. It is used to securely store data that can only be accessed by providing an access key. Mifare Classic tags used as public transport tickets, door keys, social cards, smart cards e.t.c.
Mifare Classic Tag is a type of RFID (Radio Frequency IDentification). It consists of a radio antenna with remotely powered microchip.
Mifare tags are very compact. They come in different forms like: plastic smart cards, key fobs, paper tickets, wearables, stickers. There are four types of Mifare tags with different features.
- Mifare Classic
- Mifare Plus
- Mifare Ultralight
- Mifare DESFire
Mifare Classic - widely spread, low cost, rewritable memory storage device with access keys feature. Its downside is that access keys are static. It means that if the read key is discovered by a malicious third party, then an unauthorized duplicate of Mifare Classic can be manufactured. This downside is not critical for certain applications. Some of the solutions to this problem are:
- Keeping read keys in secret, protected from unauthorized access.
- Using checksum to prevent data tampering.
- Server validation.
Mifare Plus - solves static key downside of Mifare Classic. This card can work in Mifare Classic compability mode or permanently switched to more protected mode.
Mifare Ultralight - cheapest type of Mifare. It is a croped version of MIFARE Classic. Mifare Ultralight has 64 bytes of memory and no protection with access keys. It is usually used for disposable cards. This is suitable for applications in which the tag is written only once and then used read-only.
This article focuses on Mifare Classic.
Mifare Classic comes in two memory sizes:
- Mifare Classic 1k - 1024 bytes of memory
- Mifare Classic 4k - 4096 bytes of memroy
Some of the readers that work with Mifare are:
- ACR122u
- PN532 board
- OMNIKEY
- Android Smartphone with NFC
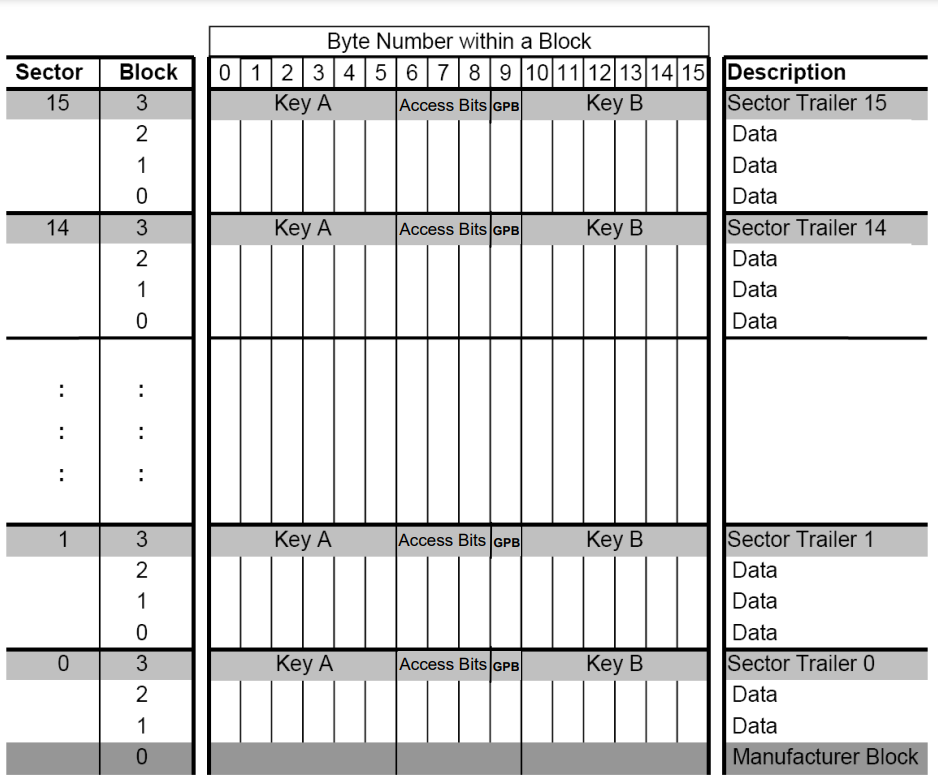
Memory structure of Mifare Classic 1K
Mifare Classic memory is organized in a certain predefined structure.
Mifare Classic 1K Memory layout:
- Consists of 1024 Bytes
- Divided into 16 Sectors with indexes from 0 to 15
- Each Sector is devided into 4 Blocks with index from 0 to 3
- Each Block contains 16 Bytes with index from 0 to 15
There are three types of blocks:
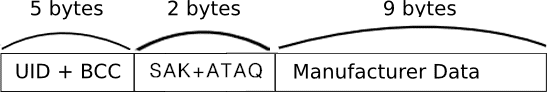
- Block 0 or Manufacturer Block. Is the first block of the first sector, block 0 of sector 0. There is only one Manufacturer Block in all memory layout. This block is predefined by Mifare provider, factory that made Mifare Cards. It is locked and cannot be altered in normal circumstances. Most of the time, applications tend to not write anything in block 0. It contains the UID and Manufacturer data. UID is a unique identifier of a card. UID can be 4 or 7 bytes long. 4 Byte UID is considered non-unique ID. Although probability to meet two same 4 Byte UID is small it is recommended to use 7 Byte UID as unique identifier of card.
- Value Block or Data Block — 16 bytes of memory which can store anything.
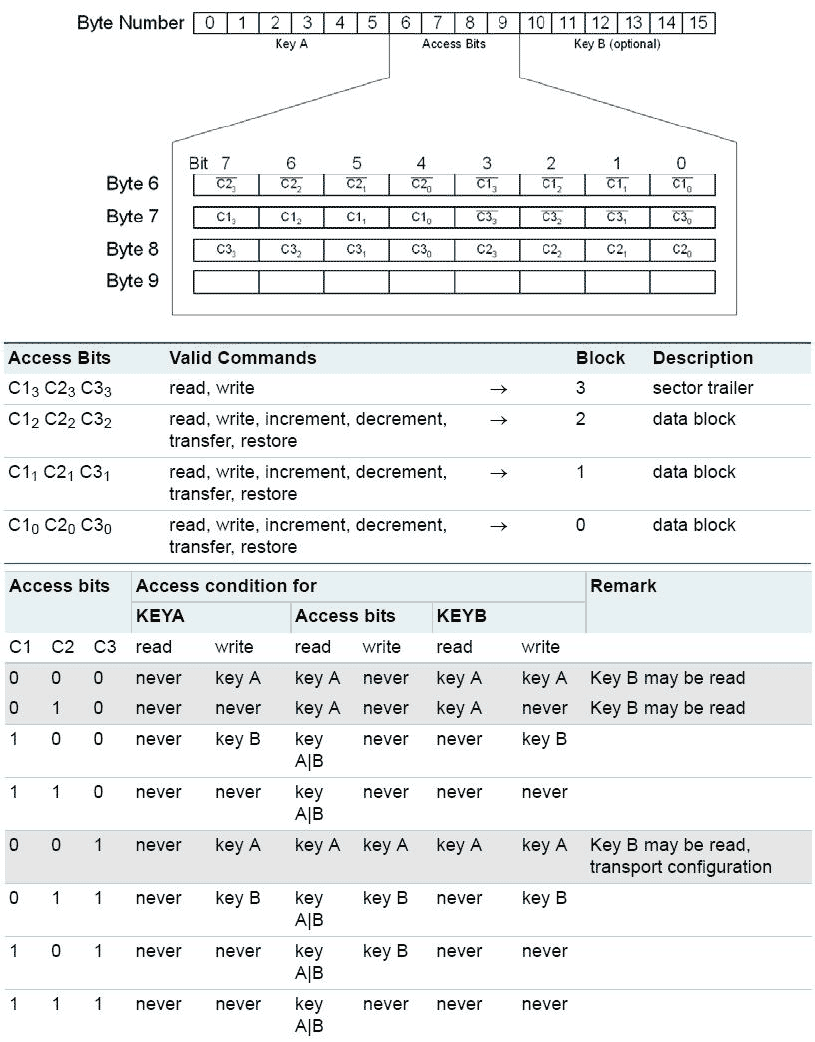
- Sector Trailer — last block, block 3, of each Sector is a Sector Trailer block. This block defines access rights of a Sector. Bytes of this block are organized in a certain predefined structure. First 6 bytes store Key A, the next 3 bytes store the Access Rights Bits, the 9th byte is a General Purpose Byte, and the last 6 bites store Key B. Key A and Key B are access keys used to read or write data. Role of Key A and Key B is defined by Access Rights Bits. A General Purpose Byte can store any value. More on Access Rights later.
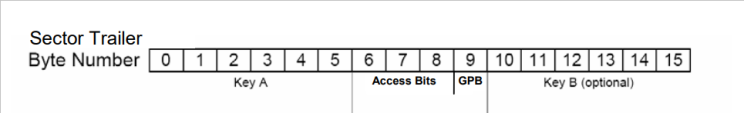
From 1024 Bytes of memory, 768 Bytes are usable. These usable bytes consists of all Value blocks and all General Purpose Bytes (16 Bytes in a Block * 3 Data Blocks in a Sector * 16 Sectors - 16 Bytes of Manufacturer Block + 1 General Purpose Byte * 16 Sectors = 768 Bytes). Other 256 Bytes of memory are used to store defined Sector Trailers and immutable Manufacturer Block.
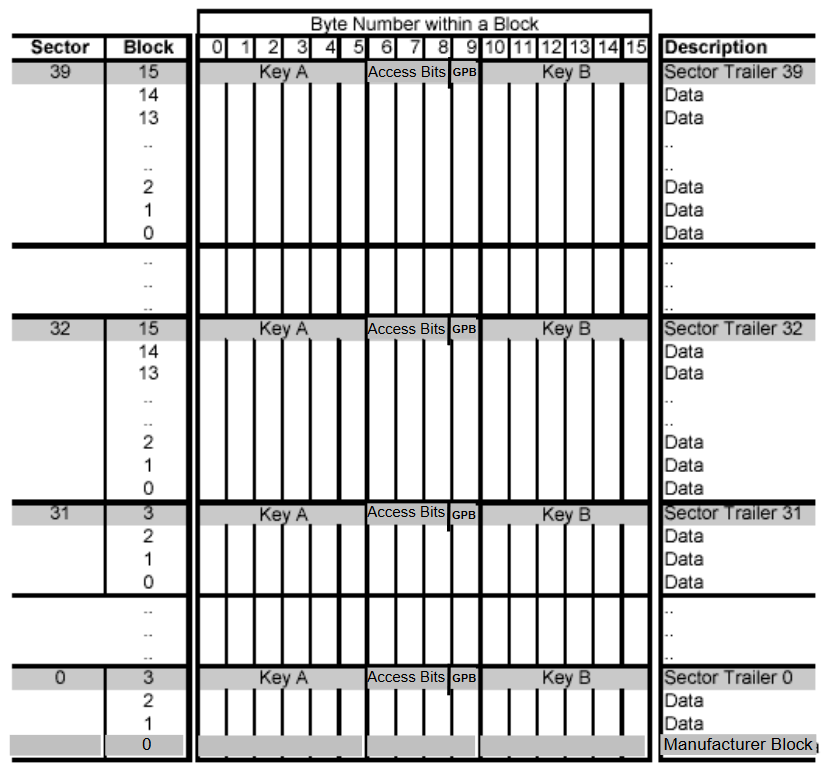
Memory structure of Mifare Classic 4K
Key concepts of Mifare Classic 4k are the same to 1K. The difference is that this type of card have more memory than the classic 1K.
Mifare Classic 4K Memory layout:
- Consists of 4096 Bytes
- Divided into 40 Sectors with indexes from 0 to 39
- 32 Sectors, from sector 0 up to sector 31 contain 4 Blocks
- 8 Sectors, from sector 32 up to sector 39 contain 16 Blocks
- Each Block contains 16 Bytes
There is more memory in the upper sectors than in the lower sector numbers.
From 4096 Bytes of memory, 3480 Bytes are usable. These usable bytes consists of all Value blocks and all General Purpose Bytes.
Other 616 Bytes of memory are used to store defined Sector Trailers and immutable Manufacturer Block.
Access rights
Mifare reader cannot read or write Mifare Classic without Authentication. Mifare reader must provide Key A or Key B in order to Authenticate. This security logic is used to protect data from tampering and unauthorized access.
For Authentication, reader must provide key same with one that is stored in the sector trailer.
All Sectors are Authorized separately, even if Keys of all Sectors are same. For example, if Mifare reader authenticated with Key A only for Sector 0, then reader cannot access Sector 15. Even if Sector 0 and Sector 15 have same keys and access bits. Reader must first authenticate to Sector 15 in order to access Sector 15.
Key A and Key B can play different roles for different blocks. Role of Key A and Key B is defined by Access Bytes.
For example following Access Bytes define Key A as read-only key and Key B as write key:
1
08778F69
MIFARE Classic 1K Access Bits Calculator (http://calc.gmss.ru/Mifare1k/) can be used to find needed Access Bytes combination.
Key value cannot be read when Access Bytes is correctly configured.
Every Sector has its own Sector Trailer. It allows to use a tag for multiple different applications. For example, Mifare Card can have sectors for medical security card, social card and public transport ticket. All these Sectors can have different keys so they can be used independently in different application. Another example of using different keys for different Sectors is an office access key that can have different Sectors for different doors and areas - Sector 0 for garage doors, Sector 1 for main doors, Sector 2 for elevator, Sector 3 for private office room, etc.
Implementation
Further information on Mifare Cards can be acquired from NXP documentation and readers documentation:
MIFARE SAM AV3 – For general purpose cryptography
android.nfc.tech.MifareClassic
ACR122U USB NFC Reader. Application Programming Interface
AN1304 NFC Type MIFARE Classic Tag Operation (amal.net/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/AN1304.pdf)
I have rich experience working with Mifare card. I have implemented application that used ACR122U USB NFC Reader to read Mifare cards on PCs and Point-of-Sale terminals. I have implemented several Android Applications that used Smartphone NFC to read and write Mifare Classic Cards. Some of them are:
- “NFP: Social Services” - Android application for social workers. For this application, I implemented Mifare reader feature.
- “NFP: Registration” - Android application for identifier issue. I implemented Mifare issue feature.
- “Lunch Place” - Application for Windows and Android. This application is used by “Lunch Place” restaurant to receive Mifare loyalty cards.
Also, I developed several Social Mifare Cards
Feel free to contact me if you need help implementing a similar feature for your Android application.
My Telegram: @SlavaGrishanin
My LinkedIn: Slava Grishanin